posted: Sep. 25, 2024.
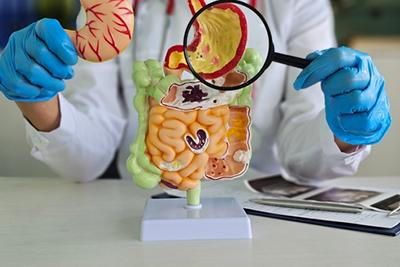
The digestive system is a complex network of organs and glands that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. Understanding how this system functions can provide valuable insight into various digestive issues and help you maintain digestive health. There are also specific issues that can affect the digestive system, and you should know what these are and when it’s time to visit your gastroenterologist for care.
Understanding Your Digestive System
The digestion system has a whole process that spans your entire digestive tract—understanding how the system works and where you might be dealing with issues. The digestive process begins in the mouth, where food is ingested. Chewing mechanically breaks down food into smaller pieces, while saliva, produced by salivary glands, contains enzymes that start the digestion of carbohydrates. Food then travels down the esophagus through a series of muscular contractions known as peristalsis. The esophagus connects the mouth to the stomach, ensuring food reaches its next destination.
Food enters the stomach through the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). The stomach’s acidic environment and digestive enzymes further break down food. From there, the chyme moves into the small intestine. The remaining undigested food and waste products enter the large intestine (colon).
Many issues can impact your digestive system, and it’s important to understand them. One common issue is acid reflux. Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. It is often characterized by heartburn, regurgitation, and a sour taste in the mouth.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can cause pain and irritation in your system. IBS is a chronic condition that affects the large intestine, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or both). Similarly, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can affect your system and make it hard to eat normally. IBD includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, both of which involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.

